Preparing for Retirement
Adapted from the FDIC’s Money Smart Program
Fact: 33% of Americans do not have any retirement savings
As you approach retirement, there are many things to think about. Experts advise that you need about 80 percent of your pre-retirement income to continue your current quality of life. The exact amount depends on your individual needs.

Important Factors to Consider:
- At what age do you plan to retire?
- Can you participate in an employer's retirement savings plan, such as a 401(k) plan, or a traditional pension plan?
- Will your spouse or partner retire when you do?
- Where do you plan to live when you retire? Will you downsize, rent, or own your home?
- Do you expect to work part-time?
- Will you have the same medical insurance you had while working? Will your coverage change?
- Do you want to travel or pursue a new hobby that might be costly?
Pro Tip: Use this calculator to help you plan ahead
The three most common options to save for retirement are: retirement plans offered by an employer, savings and investments, and social security
Your Employer’s Retirement Plan
If your employer offers a retirement plan, such as a 401k, sign up and contribute as much as you can. Compound interest and tax deferrals make a huge difference over time, so take advantage as soon as you’re eligible. Taxes may be lower, and your company may contribute as well.
401k Retirement Plan
A 401k is a retirement savings account that allows an employee to divert a portion of their salary into a long-term investment account. Your employer may match up to a certain limit and the account may be eligible for special tax benefits under the IRS guidelines. When signing up for a 401k, employees typically must wait until they are 59 ½ years of age to withdraw funds without a tax penalty.
Fact: Fewer than half of Americans have calculated how much they need for retirement
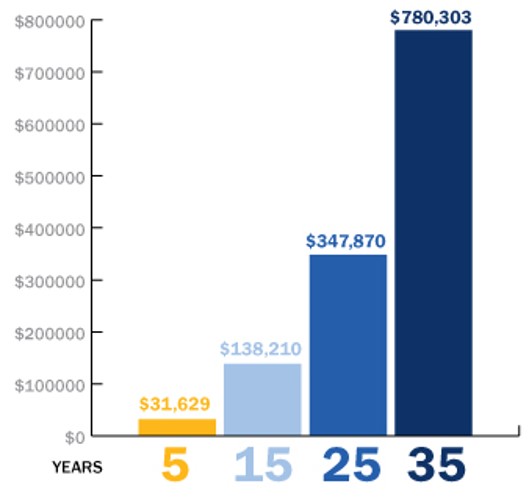
The advantage of starting early: Start now! The chart below shows what you would accumulate at 5, 15, 25, and 35 years if you saved $5,500 each year and your money earned 7% annually.
Savings and Investments
Your personal savings and investments can also be used to provide income in retirement. These do not always have the tax advantages of formal retirement plans but are an important part of your overall financial strategy. An Emergency Savings can help prevent dipping into your retirement plan if you have a sudden unexpected expense or suffer a sudden job loss.
Fact: The average American spends roughly 20 years in retirement.
Individual Retirement Accounts
You can currently contribute up to $6,000 per year into a personal IRA. And, you can participate in both your 401k at work and a personal IRA if your income is below $75,000 (or $124,000 for couples). If you’re 50 years of age or older, you can contribute even more.
There are two types of IRA accounts:
- Traditional
- Pro: if deductible, contributions lower taxable income in the year they are made
- Cons: deductions may be phased out and distributions in retirement are taxed as ordinary income
NOTE: Unless you meet an exception, early withdrawals of contributions and earnings are taxed and subject to a 10% penalty.
- Roth
- Pros: qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free and contributions can be withdrawn at any time
- Cons: there is no immediate tax benefit for contributing and the ability to contribute is phased out at higher incomes
NOTE: Contributions can be withdrawn at any time, tax-and penalty-free. Unless you meet an exception, early withdrawals of earnings may be subject to a 10% penalty and income taxes.
Fact: 19% of people ages 65 and older were working as of 2017 and 20% of workers say they’ll never be able to retire
Social Security Benefits
Social Security Benefits an average equal roughly 40% of what you earned before retirement. Use the retirement estimator here: www.socialsecurity.gov
When planning and preparing for retirement, be sure to consider basic investment principles. Inflation and the type of investments you make can play a huge role in how you will have when it comes time for you to retire. Ask questions, seek to understand how your savings or pension plan is invested, and diversify. Remember, financial security and knowledge go hand-in-hand.
